|
|
|
|
First of all, quantum algorithms are written in a mathematical way.
This kind of representation, with texts and symbols, is quite appropriate in a theoretical point of view,
but it doesn't allow an easy implementation if you want to program a simulation on a classical machine.
|
|

extract from a Richard Jozsa's course
|
|
|
|
|
Another way to represent quantum algorithms is often used: a hybrid of graphics and mathematical symbols.
But such representations are sometimes not very accurate, like the ellipse that show interferences in this particular image.
|
|
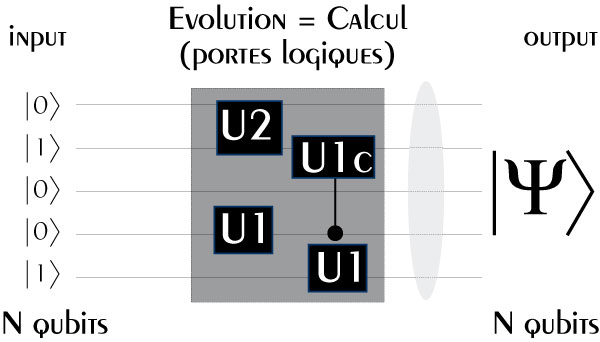
extract from "Quantum computer,
twelve years after Shor", Valerio Scarani
|
|
|
|
|
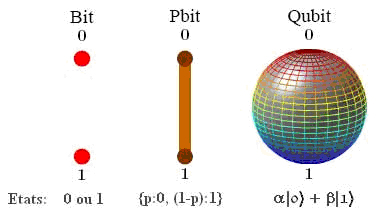
In a more elementary point of view, qubits are usually represented by a 2-dimensional vector.
This is very simple and easy to understand. The drawback is, that for a non-expert, it is difficult to remember that each coefficient
corresponds in fact to the modulus of the complex magnitude.
|
|

extract from a Frédéric Magniez's course
|
|
|
|
|
To compromise for the previous problem, the qubit can be represented as a sphere, the Bloch's sphere,
which shows the complex magnitudes with 2 angles.
Unfortunately, such representations don't exist for higher dimensions.
|
|
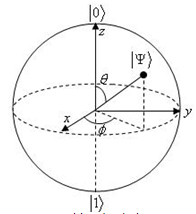
preview from any initiation
about quantum computing
|
|
|
|
|
Some attempts were made to use colors.
Either with the blend of 2 colors...
|
|

extract from an article of
Scientific American, Nov 2002
|
|
|
|
|
|
... or with very different colors...
|
|
images from various articles
futura-sciences, sup-info, aso.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lastly 2 colors - Green and Red - are sometimes used to represent the two base-vectors |0> et |1>.
|
|
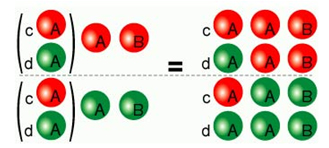
image obtained from a course at
Sherbrooke University.
|